基础入门
Elasticsearch 是一个近实时的分布式搜索分析引擎。
- 一个分布式的实时文档存储,每个字段 可以被索引与搜索
- 一个分布式实时分析搜索引擎
- 能胜任上百个服务节点的扩展,并支持 PB 级别的结构化或者非结构化数据
安装并运行Elasticsearch
首先安装java
1 | yum install java |
下载Elasticsearch
1 | $ wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-5.5.1.zip |
https://mirrors.huaweicloud.com/elasticsearch/7.10.1/
启动Elasticsearch
https://www.cnblogs.com/brady-wang/p/13233021.html
1 | $ ./bin/elasticsearch |
如果你想把 Elasticsearch 作为一个守护进程在后台运行,那么可以在后面添加参数 -d 。
启动时,可以指定pid文件
1 | ./bin/elasticsearch -d -p pid |
此时要关闭,只需要
1 | pkill -F pid |
即可。
测试是否成功
1 | curl 'http://localhost:9200/?pretty' |
成功会输出响应:
1 | { |
这就意味着你现在已经启动并运行一个 Elasticsearch 节点了,你可以用它做实验了。 单个 节点 可以作为一个运行中的 Elasticsearch 的实例。 而一个 集群 是一组拥有相同 cluster.name 的节点, 他们能一起工作并共享数据,还提供容错与可伸缩性。可以在elasticsearch.yml中修改cluster.name。
kill elasticsearch
1 | ps -ef | grep elastic |
找到对于进程
1 | kill -9 |
杀掉进程。
更改端口号
更改elasticsearch.yml文件中的
1 | http.port: 8200 |
在浏览器中访问ES
更改elasticsearch.yml文件中network.host为
1 | network.host: 0.0.0.0 |
重启,此时可以直接在浏览器中使用http://IP:PORT进行访问。同时可以在插件elasticsearch-head中设置连接。
一些重要设置
path设置
在elasticsearch.yml中设置path:
1 | path: |
集群名
在elasticsearch.yml中设置
1 | cluster.name: logging-prod |
节点名
在elasticsearch.yml中设置
1 | node.name: prod-data-2 |
主机设置
默认es绑定环绕地址,例如127.0.0.1and[::1]。要与其他服务器上的节点形成集群,您的节点将需要绑定到非环回地址,例如:
1 | network.host: 192.168.1.10 |
network.host节点将绑定该地址,并向集群中其他节点广播。
当提供了非默认的network.host设置,es将从开发模式切换到生产模式。
更多主机设置看:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/modules-network.html
传输层
当用户使用HTTP请求es时,es接收到客户端请求的节点不能总是单独处理它,而通常必须将其传递给其他节点以进行进一步处理。实现方式为使用网络传输层,改传输层时集群中节点通信方式。
使用transport进行设置。具体查看https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/modules-transport.html
network配置用来绑定地址接受请求。收到请求后,按照transport的配置转发请求到实际处理的地址。
集群发现设置
discovery.seed_hosts
默认情况下,es将绑定回绕地址,并扫描本机9300-9305去连接其他运行中的节点。
当相要通过与其他主机的其他节点连接来组成集群时,需要使用静态discovery.seed_hosts设置。该设置提供一个其他主机的节点列表,这些节点符合主机资格,并且可能处于活动状态并且可以联系以执行发现过程。例如:
1 | discovery.seed_hosts: |
对于未提供port的主机,默认端口为9300.
对于域名解析存在多个ip的,会依次扫码所有主机。
IPv6地址必须放在方括号中。
cluster.initial_master_nodes
在集群第一次启动时,启动引导程序将决定一个在第一次选举中投票将被统计的符合主节点的集合。对于开发模式来说,这一步是节点自动完成的。
对于生产模式来说,自动意味着不可靠,因此在生产模式下第一次启动集群,需要指明在第一次选举中投票将被统计的主节点的集合。配置例如:
1 | discovery.seed_hosts: |
在集群首次成型后,从每个节点的配置移走cluster.initial_master_nodes。在重启集群或增加新节点时,不应该有cluster.initial_master_nodes配置。
重要的系统设置
理想状态下,es应该运行在一个单独的机器上,并且能够使用获得到的所有资源。因此,需要设置一下系统配置,已使es能够访问的资源超过默认值。
开发状态和生产状态
默认,es运行在开发状态,此时如果任何配置没有正确配置,警告信息会写入log,并且启动节点。
一旦配置了网络信息,例如network.host。es认为进入生产状态。并且将之前的警告信息抛出异常。异常将使节点启动失败,保证数据不会丢失。
系统设置
更多系统设置查看https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/system-config.html
ulimit
设置打开文件句柄最大数量
1 | sudo su |
使用ulimit -a查看当前限制。
启动检查
单节点发现
我们认识到某些用户需要将传输绑定到外部接口以测试其对传输客户端的使用。这时,es提供单节点发现,设置discovery.type 为single-node。此时,节点将选举自己为主节点,并且不会与任何其他节点一起加入群集。
强制启动检查
在生产模式下运行一个单节点,如果未绑定transport为一个外部地址,或者绑定外部地址,但设置了单节点发现,就会避开启动检查。如果希望强制进行启动检查,可以配置es.enforce.bootstrap.checks to true。(JVM设置https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/jvm-options.html)。
启动X-PACK检查
如果使用了加密数据,需要进行密钥检查。具体看:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/bootstrap-checks-xpack.html#_pki_realm_check
节点发现和集群构建
具体参考https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/6.8/modules-discovery-zen.html
选举master节点:https://www.nosuchfield.com/2019/03/18/How-Elasticsearch-elected-the-master/
使用RESTful API和http与Elasticsearch交互
使用 RESTful API 通过端口 9200 和 Elasticsearch 进行通信。使用 curl 命令来和 Elasticsearch 交互。一个 Elasticsearch 请求和任何 HTTP 请求一样由若干相同的部件组成:
1 | curl -X<VERB> '<PROTOCOL>://<HOST>:<PORT>/<PATH>?<QUERY_STRING>' -d '<BODY>' |
被 < > 标记的部件:
VERB |
适当的 HTTP 方法 或 谓词 : GET、 POST、 PUT、 HEAD 或者 DELETE。 |
|---|---|
PROTOCOL |
http 或者 https(如果你在 Elasticsearch 前面有一个 https 代理) |
HOST |
Elasticsearch 集群中任意节点的主机名,或者用 localhost 代表本地机器上的节点。 |
PORT |
运行 Elasticsearch HTTP 服务的端口号,默认是 9200 。 |
PATH |
API 的终端路径(例如 _count 将返回集群中文档数量)。Path 可能包含多个组件,例如:_cluster/stats 和 _nodes/stats/jvm 。 |
QUERY_STRING |
任意可选的查询字符串参数 (例如 ?pretty 将格式化地输出 JSON 返回值,使其更容易阅读) |
BODY |
一个 JSON 格式的请求体 (如果请求需要的话) |
计算集群中文档的数量,我们可以用这个:
1 | curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9200/_count?pretty' -d ' |
JSON
Elasticsearch使用json作为文档的序列化格式。
存储
存储路径包含三部分信息。分别为索引名称、类型名称、一条数据(大致对应于mysql里的database,table和一行数据)。在Elasticsearch中索引有两种含义:
- 索引(名词):一个 索引 类似于传统关系数据库中的一个 数据库 ,是一个存储关系型文档的地方。 索引 (index) 的复数词为 indices 或 indexes 。
- 索引(动词):索引一个文档 就是存储一个文档到一个 索引 (名词)中以便被检索和查询。这非常类似于 SQL 语句中的
INSERT关键词,除了文档已存在时,新文档会替换旧文档情况之外。
Elasticsearch还存在倒排索引,增加检索速度。与业务中大致相同。
建数据
索引一条信息到Elasticsearch语法可以为:
1 | curl -XPUT "http://localhost:8222/megacorp/employee/3" -d '{ |
索引数据
1 | curl -XGET "http://localhost:8222/megacorp/employee/3" |
轻量搜索
请求某一层级下所有数据:
1 | curl -XGET "http://localhost:8222/megacorp/employee/_search" |
返回结果不仅告知匹配了哪些文档,还包含了整个文档本身:显示搜索结果给最终用户所需的全部信息。
增加简单约束搜索:
1 | curl XGET "http://localhost:8222/megacorp/employee/_search?q=last_name:Smith" |
更复杂搜索
使用过滤器:curl XGET “http://localhost:8222/megacorp/employee/_search“ -d ‘
1 | curl XGET "http://localhost:8222/megacorp/employee/_search?pretty" -d ' |
全文搜索
搜索喜欢攀岩的员工
1 | curl XGET "http://localhost:8222/megacorp/employee/_search?pretty" -d ' |
Elasticsearch 默认按照相关性得分排序,即每个文档跟查询的匹配程度。
短语搜索
执行这样一个查询,仅匹配同时包含 “rock” 和 “climbing” ,并且 二者以短语 “rock climbing” 的形式紧挨着的雇员记录。
使用一个叫做 match_phrase 的查询
1 | curl -XGET "http://10.138.35.116:8222/megacorp/employee/_search?pretty" -d ' |
高亮搜索
应用都倾向于在每个搜索结果中 高亮 部分文本片段,以便让用户知道为何该文档符合查询条件。在 Elasticsearch 中检索出高亮片段也很容易。
再次执行前面的查询,并增加一个新的 highlight 参数:
1 | curl XGET "http://localhost:8222/megacorp/employee/_search?pretty" -d ' |
此时输出为
1 | { |
可以看到,about匹配部分被标记出来。
分析
Elasticsearch 有一个功能叫聚合(aggregations),允许我们基于数据生成一些精细的分析结果。聚合与 SQL 中的 GROUP BY 类似但更强大。
分析员工年龄(中文文档可能比较旧了,有问题,不能分析喜好,由于interests是text,不能进行聚合分析):
1 | curl XGET "http://localhost:8222/megacorp/employee/_search?pretty" -d ' |
索引模块
索引模块是为每个索引创建的模块,用于控制与索引相关的所有方面。
索引级别的设置可以对每个索引设置。设置有两种方式:
- 静态设置:创建索引时或者对一个关闭状态的索引。
- 动态设置:被设置在索引工作中,使用更新索引设置的API
静态索引设置
下面是所有索引通用的静态索引设置(部分)。
index.number_of_shards
索引中主分片数量。默认1。只能在创建时设置。最大1024.可以使用export ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Des.index.max_number_of_shards=128"更改限制。
索引中数据的存放是按照(_id)%nubber_of_shards来决定分片的。
index.number_of_routing_shards
路由分片数量被用来切割一个索引。由于前期我们对整体认识的不足,可能导致主分片数量分片过少,影响整体吞吐速度。这时可以通过对分片进行切割,增加主分区数控。例如,对于一个存在5个主分区的索引。切割为30个。此时分割可能有三种方式
1 | 5->10->30(依次拆分为2和3) |
进行此操作,要求索引是只读的,且集群是绿色的。
用法为
1 | POST /<index>/_split/<target-index> |
<index>为要被切割的索引。<target-index>为切割后索引的名字。
查看当前设置:
1 | curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XGET "localhost:8233/bank/_settings?pretty" |
设置为只读
1 | curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPUT "localhost:8233/bank/_settings?pretty" -d '{ |
进行切割
1 | curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPUT "localhost:8233/bank/_split/bank_test?pretty" -d ' |
查看当前切割进展
1 | curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XGET "localhost:8233/_cat/recovery/bank_test" |
查看新索引分片数量
1 | curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XGET "localhost:8233/bank_test/_count" |
index.codec
存储数据压缩方式,默认是LZ4。可以设置为best_compress。此时会有更高的压缩率,代价是更慢的过程。
动态索引设置
index.number_of_replicas
每个主分片副本数量。默认是1。
index.search.idle.after
分片在被视为搜索空闲之前无法接收搜索或获取请求的时间。
索引屏蔽
索引屏蔽用来限制一类操作。允许限制读、写、元数据。设置方式为:
1 | PUT /<index>/_block/<block> |
<index>索引名称的逗号分隔列表或通配符表达式,用于限制请求。
<block>有如下几种
| 设置 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| metadata | 不能更改元数据,例如关闭索引。 |
| read | 不能进行读操作 |
| read_only | 不能进行写操作和元数据变更 |
| write | 不能进行写操作 |
| read_only_allow_delete | 可以进行读操作和删除索引 |
该操作会时对应的block变成true。例如
1 | $ curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPUT "localhost:8233/bank/_block/write?pretty" |
恢复设置通过:
1 | PUT /index/_settings |
例如:
1 | curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPUT "localhost:8233/bank/_settings?pretty" -d '{ |
合并
一个Elasticsearch分片就是一个Lucene索引,Lucene索引被分解成段。分段是索引中存储索引数据的内部存储元素,并且是不可变的。较小的段被定期地合并成较大的段,以保持索引的大小和清除被标记为删除的文档。合并过程使用自动调节来平衡合并和其他活动(如搜索)之间的硬件资源的使用。
合并运行在单独的线程中,并且当达到最大线程数时,更多的合并将等待直到合并线程可用。
合并支持动态设置
1 | index.merge.scheduler.max_thread_count |
单独的一个分片中一次合并时的最大线程数。默认为MAX(1, MIN(4, <<node.processors, node.processors>>/2))。
相似模块
相似模块定义了如果计算文档相关性评分。每个字段具有相似性,这意味着可以通过映射为每个字段定义不同的相似性。
在创建索引和更新索引时,我们可以设置相似模块。例如:
1 | PUT /index |
1 | curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPUT "localhost:8233/similarity_test" -d ' |
这里我们通过es提供的基础DFR相关性模块生成了一个自己的my_similarity相关性模块。之后订阅使用my_similarity订阅文档结构:
1 | PUT /index/_mapping |
1 | curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPUT "localhost:8233/similarity_test/_mapping?pretty" -d ' |
下面列举ES提供的基础相似模块。
BM25相似
type:BM25
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Okapi_BM25
DFR相似
type:DFR
DFI相似
type:DFI
IB相似
type:IB
LM相似
type:LMDirichlet
Scripted相似
type:scripted。
通过自己脚本计算评分。例如:
1 | PUT /index |
其中weight_script是可选,该部分返回weight,即权重。其中使用的字段为ES默认脚本语言。详见:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/painless/7.9/painless-similarity-context.html。
此时增加数据
1 | PUT /index/_doc/1 |
搜索并返回排序依据
1 | GET /index/_search?explain=true |
搜索后面加explain=true用来返回排序依据。返回如下
1 | { |
默认相似
默认情况下,es将使用默认配置的相似。默认相似可以在创建索引时设置。
1 | PUT /index |
如果想要更改一个索引的默认相似,需要先关闭节点,再更改。
1 | POST /index/_close |
事务日志
由于向Lucence提交数据才能将数据持久化到磁盘上,但提交数据到Lucence代价是十分高昂的。因此ES是将一组数据一起提交(提交到Lucence前先放到内存里,不可搜索,可以通过id获取)。但为了防止未持久化的数据丢失,需要建立一个事务日志,将还未持久化的操作记录下来。
flush就是将数据提交到Lucence,并生成一个新的事务日志。flush操作是自动为了防止事务日志过大。
存在事务日志中的数据在被同步和提交后,会被持久化。如果在持久化前,操作系统出现故障,会导致存在内存中还未提交的更改丢失,此时重启分片,会先读取事务日志,保证数据正常。
默认设置下index.translog.durability是request,即,每次的index delete update bluk请求都会在日志文件被同步并且提交到主分片和被分配的副分片后才返回。如果index.translog.durability是async,即是异步的,则事务日志被每index.translog.sync_interval提交。这可能导致节点错误后恢复,部分操作丢失。
index.translog.sync_interval
异步情况下,事务日志被提交周期。默认5s。至少100ms。
index.translog.durability
输完同步方式。
request:同步。
async:异步。
index.translog.flush_threshold_size
事务日志可接受最多大小,当超过该值时会进行同步。默认512mb。
历史记录保留
es有时需要重入一些操作。例如,一个副分片出现短暂的离线,主分片在这段时间的操作需要在副分片重新执行,以保证副分片的数据正常。在跨集群复制也是一样的。
在Lucence层只有两种操作。写和删除(更新是删除加写)。对于写来说,Lucence文档本身就包含重新执行所需要的内容,但对于删除来说,Lucence不包含。ES为解决该问题,使用软删除(soft delete)机制。即删除并未被真正的删除。
ES只保留最近确定的删除,因为软删除依然占用空间。最终,ES还是会将数据删除。ES不需要重复执行所有操作,其只需要记录将来需要重复执行的操作即可。
ES保持使用被称为分片历史记录保留租约的机制来跟踪将来需要重复执行的操作。每一个分片副本首先需要创建一个分片历史租约。分片副本可能是一个副分片,或者在跨集群负责中相对于leader分片的follower分片。每个分片历史租约跟踪第一个当前分片还未执行的序列号。一旦该分片执行了对应序列号的操作,就将(自己的)序列号增加,来标识该序列号对应的操作自己不需要在执行了。当所以分片历史保留租约都不包含某个序列是,该序列对应的操作可以丢弃。(整体类似精简版的TCP协议)。
如果一个分片发生错误并且停止增加自身的序列号,ES将保存所以数据。但分片历史记录保留租约是存在时效的。如果一个分片在时效期内未正确接收到操作,租约将会时效。该机制保护ES不会永久存储这些信息,因为一旦租约失效,ES可以丢弃对应的历史信息。如果分片副本在其保留租约到期后恢复,则Elasticsearch将退回到复制整个索引,因为它不再能够简单地重播丢失的历史记录。
index.soft_deletes.enabled标识是否启用软删除,默认是true。
index.soft_deletes.retention_lease.period。租约到期时间,默认12h。
索引排序
在我们创建索引时,我们可以控制段落在分片中的排序。nested不支持作为设置参数。
例如:
1 | PUT my-index-000001 |
1 | PUT my-index-000001 |
index.sort.field
作为排序依据的字段列表。只支持bool,numeric,date,keyword,doc_values。
index.sort.order
排序类型。asc:升序。desc:降序。
index.sort.mode
对于多个字段排序来说,支持设置培训模式。
min:选取最小值进行排序。
max:选取最大的进行排序。
index.sort.missing
missing参数指定应如何处理缺少该字段的文档。 缺少的值可以具有以下值:
_last:不存某个字段,排在最后。
_first:不存某个字段,排在最前。
Mapping
mapping被用来定义一个文档中包含的字段类型、如何被存储、如何被检索。
一个mapping的定义包含元数据(matedata)域和字段数据。
为了防止mapping爆炸,定义了一些限制条件。
设置
index.mapping.total_fields.limit
一个索引中包含的最多字段数量。默认1000
index.mapping.depth.limit
字典最大深度。默认20.
index.mapping.nested_fields.limit
一个索引中被明确表示为嵌套的字段的最大数量。默认50
index.mapping.nested_objects.limit
在索引的所有嵌套域中能够包含的字段数量。默认10000.
index.mapping.field_name_length.limit
字段名最大长度。默认无限制。
使用显式映射创建索引
1 | PUT /my-index-000001 |
在已经存在的映射中增加字段
使用put mapping API:
1 | PUT /my-index-000001/_mapping |
更新字段的映射
除了支持映射参数(mapping parameters)外,不能更改已存在字段的映射或者字段类型。
想要重命名一个已存在的字段也是不合理的,应该别名来创建一个合理的字段名。
查看一个索引的映射
使用get mapping API
1 | GET /my-index-000001/_mapping |
查看索引中特定字段的映射
使用get field mapping API
1 | GET /my-index-000001/_mapping/field/employee-id |
移出映射类型
对于老版本的ES来说,索引组织结构为<index>/<type>/<_id>。设计初衷是为了与SQL的database,table,行三层结构对应。但SQL中,不同table里的同样字段是没有关系的,但在ES中,不同类型的同样字段要求数据映射是一样的,这不是十分合理。例如,在同一个索引中,deleted字段在一个类型中希望是日期类型,在另一个类型中希望是bool类型,但之前的ES是不支持的。因此,新版本会删除类型。
为此,提出了如下替代方案。
每个索引一个文档类型
每一个索引只有一种类型。
好处是数据更方便被压缩,全文本索引时加速。
对于关系类数据来说,我们应该使用join field(联合字段)。
用户类型
有时我们为了充分利用分片的资源,希望在一个索引下建立多个类型,也是允许的。例如
1 | curl -XPUT "localhost:8233/twitter?include_type_name=false&pretty" -d ' |
好像不太好使,还是不建议一个索引多个类型。
无类型API
索引API
索引创建、索引模板和mapping API都支持include_type_name的url参数。默认为true。表示在请求和相应时是否包含类型名。
例如:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000001?include_type_name=false&pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000001/_mappings?include_type_name=false&pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/my-index-000001/_mappings?include_type_name=false&pretty" |
文档API
在新版本的ES中,要自动创建_id,索引API必须使用{index}/_doc路径。对于指定了id的文档来说,url路径为{index}/_doc/{id}。
例如:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000001/_doc/1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/my-index-000001/_doc/1?pretty" |
_doc在新版的ES中代替了type作为终点名。
API路径可以包含终节点_updata,_source.
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/my-index-000001/_update/1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
搜索API
当调用_search,_msearch,_explaini,url路径中不应该包含type。
索引模板
当创建一个索引模板是,我们也可以设置include_type_name。但最终生成的索引是否包含类型取决于创建索引的调用,而与索引模板没有关系。例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/_template/template1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
这里,虽然index-1-01匹配的模板是template1,模板是无类型的,但index-1-01是有类型的。同样,index-2-01匹配的是模板是template2,虽然模板是有类型的,但index-2-01是无类型的。
字段数据类型
包括常见类型binary,boolean,Keywords,Number,dates,alias.
object和关系类型object,flattened,nested,join.
结构数据类型Range,ip,version,murmur3.
分析数据类型histogram
文本搜索类型text,annotated-text,completion,search_as_you_type,token_count.
其他类型percolator.
数组类型arrays
多类型支持。
Alias(别名)
定义了一个在索引中字段的别名。例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/trips?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
别名的路径path要求是完整路径,例如object1.object2.field.
大多数内容都支持别名。别名的目标存在限制:
- 目标必须是确定类型,不能是object或者是别名。
- 目标必须存在
- 如果定义了嵌套对象,则字段别名必须与其目标具有相同的嵌套作用域。
别名不支持的API:
向别名写是不支持的,尝试用别名索引(建数据)或者更新是不被允许的。别名不能被用来作为
copy_to的目标或者multi-fields。由于别名不会出现在源文档中,别名不能用来进行源数据过滤,例如
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8curl -X GET "localhost:8233/trips/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query" : {
"match_all": {}
},
"_source": "route_length_miles"
}
'
Array(数组)
ES没有专门的array类型数据。任何字段可以包含零个或多个值。然而在数组中所有值必须有相同的类型,例如
["one", "two"][1,2][1,[2,3]]和[1,2,3]是一样的。- [
{ "name": "Mary", "age": 12 },{ "name": "John", "age": 10 }]
对象数组往往不能像我们期待的那样工作,不能单独的请求数组中的每个对象。如果需要,应该使用nested类型代替object。
动态的增加一个字段,第一个值将决定该字段类型。剩下的值要么和这个值类型一样,要么可以进行转换到该类型。例如[0,"striing"是不被支持的。
数组可以包含空值,这些空值要么被配置的null_value替换,要么被完全跳过。空数组[]被视为缺少字段-没有值的字段。
例如:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000001/_doc/1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
第一个索引tag被设置为一个数组,list被设置为一个对象数组。第二个索引不包含数组。第三个请求那个品牌上述两个文档。
Binary(二进制)
binary类型支持一个被Base64编码的二进制字符串。默认情况下,ES不存储二进制字段,也不能用来搜索。
binary字段支持的参数
doc_values:该字段是否应该以多列的方式存储在磁盘上,以便以后可以用于排序,聚合或编写脚本?接受参数ture|false(default).
store:是否应该存储该字段并与_source分开检索。接受参数ture|false(default).
Boolean(bool类型)
bool类型可接受的值为:
| False values | false "false","" |
|---|---|
| True values | true,"true" |
汇总分析中,例如terms汇总使用0和1作为值。当使用脚本时,boolean字段返回0和1.
其可接受的参数为:
| 参数 | 默认 |
|---|---|
boost |
1.0 |
doc_values |
true |
index |
true |
null_values |
null表示不配置 |
store |
false |
meta |
Date类型字段
JSON不存在日期数据类型。日期在ES能够被表示如下:
- 字符串,例如
2015-01-01 - 长数值为毫秒的时间戳。
- int表示秒的时间戳。
在内部,日期被转化为长数值的时间戳。请求时,日期在内部被转换为一个range,分析和存储的结果返回前被转化回去。
日期的格式能够被用户使用form参数自定义,如果未定义,则使用默认值strict_date_optional_time||epoch_millis.(具体参加form)。
日期的格式支持多格式,多个日期格式使用||分割,每个日期格式都会被尝试,直到找到第一个匹配的。例如:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
date支持参数:
| 参数 | 默认值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
boost |
1.0 | ||
doc_values |
false | ||
format |
strict_date_optional_time\ | \ | epoch_millis |
locale |
|||
ignore_malformed |
False | ||
index |
Truw | ||
null_value |
丢失值 | ||
store |
False | ||
meta |
Dense Vector字段类型
一个dense_vector字段存储压缩的float数组。最大纬度为2048.
该向量那个被用来计算文本相关性(使用script),例如可以使用query中的向量和文档中的向量距离作为一个文本的相关性。
例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
在内部,每个文档的压缩向量被编码作为一个二进制文本值。尺寸为4*dim+4。
keyword类型
keyword类型包含三种。
keyword:用于结构化数据,例如ID,email等。
keyword被用来排序,分析和term级别的请求。应该避免使用keyword进行全文本搜索,而使用text。
数值不一定都要使用numeric类型,对于不使用range进行搜索,并且更快的召回是更重要的时,使用keyword是更合适的,因为term搜索keyword相比与term搜索numeric是更快的。如果不确定到底使用何种类型,可以使用多类型。
keyword支持的参数
| 参数 | 默认值 |
|---|---|
| boost | 1.0 |
| Doc_values | True |
| Eager_global_ordinals | False |
| Fields | 未设置 |
| Ignore_above | 256 |
| Index | true |
| Index_options | docs |
| Store | false |
| Similarity | BM25 |
| Null_value | miss |
constant_keyword是特殊的keyword,为常值,每个doc该字段值是一样的。
1 | PUT logs-debug |
对于索引文档时,如果没有设置level自动,默认使用debug填充,如果设置了,则必须为debug。
wildard:通配符类型
通配符类型可以优化在请求时是通配符的速度。通配符在其他类型字段也是可以的但是存在限制。
- text:text字段将任何通配符表达式的匹配限制为单个标记,而不是字段中保存的原始整个值。
- keyword:匹配速度慢。
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
Flattened字段类型
默认情况下,在一个object中,每个子字段被单独的mapped和indexed。如果子字段是未知的,则使用动态映射。
flattened提供一个可选方式,将整个object映射作为一个单独的字段。flattened解析所有object中页节点的值,并且索引他们到一个字段下,作为keywords。object的内容能够通过请求和分析进行搜索。例如:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/bug_reports?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
请求
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/bug_reports/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
flattened支持的请求操作:
term,terms,terms_set
prefix
range
match, multi_match
query_string,simple_query_striing
exists
支持的参数:
| 参数 | 默认值 |
|---|---|
| boost | 1 |
| doc_value | Default |
eager_global_ordinals |
False |
ignore_above |
Unlimit |
| Index | True |
| Index_options | Docs |
| Null_valuse | Miss |
| Similarity | BM25 |
Geo-point类型
geo-point接受latitude-longitude对,用来标识定位。其主要用途如下:
- 在边界框内、中心点一定距离内、多边形内或geo_shape查询中查找地理点。
- 分析文档地理位置。
- 将地理位置作为评分依据。
- 按距离排序。
如下列出支持的方式
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
在脚本中使用定位
1 | def geopoint = doc['location'].value; |
join类型
join类型用来表示在同一索引下的关系数据。一个关系数据定义如下:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
这里question是父,answer是子。
在索引含有join的文档时,要在source中表明其是父还是子:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001/_doc/1?refresh&pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
在索引子关系是,要表明其父的id是多少,一个父可以对应多个子,但一个子只能对应一个父:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001/_doc/3?routing=1&refresh&pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
ES的关系和关系数据库的关系不同,使用场景也不一样。关系数据存在一定限制:
- 一个索引只能存在一个join
- 父子必须在相同分片。
- 父可以有多个子,子只能有一个父。
多父子关系:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
这里question是answer和comment的父。
多层级关系
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
这里question是answer和comment的父。而answer是vote的父。
Nested类型
nested是特殊的object类型。其允许object类型的数组以彼此独立查询的方式对每个元素请求。
ES没有对象(object)内部的概念。因此,它打平对象等级进入一个简单的field和value数组。例如:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000011/_doc/1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
在内部,这个文档将被存储类似如下:
1 | { |
此时名字将的关系将丢失。此时将错误的匹配alice和smith查找:
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/my-index-000011/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
当想要索引object数组并且维持每个数组中元素独立。此时应该使用nested。
在内部,nested对象索引每个object数组元素为一个隐藏的文档,这意味着,每个nested对象能够独立的被请求,使用nested请求。
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000012?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
此时第一个search将返回空,即无匹配,第二个请求将返回文档1.
nested支持的参数。
- dynamic:默认true。
- properties。
numeric(数值类型)
数组类型有如下几种
| 类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| long | 64位长整型 |
| Integer | 32位整型 |
| Short | 16位短整型 |
| Byte | 1位,8bit(-127, +127) |
| Double | 64位双精度浮点数 |
| Float | 32位单精度浮点数 |
| Half_float | 16位半精度浮点数 |
| Scaled_float | 使用long存储的双精度浮点数,指明缩放因子(scaling_factor),使用时与浮点数一样,内部存储优化。 |
| Unsigned_long | 无符号64位长整型。 |
使用如下:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
数字类型支持的参数:
| 参数 | 默认值 |
|---|---|
| Coerce | true |
| boost | 1 |
| Doc_values | true |
| Ignore_malformed | false |
| Index | true |
| Null_values | 未设置 |
| Store | false |
| Meta |
object类型
JSON文档本质上是分层的:文档可能包含内部对象,而内部对象又可能包含内部对象本身。object支持的参数为:
| 参数 | 默认值 |
|---|---|
| dynamic | true |
| properties | |
| enabled | true |
precolcolator类型
range类型
range表示连续范围。使用gt或gte表示下边界,lt或lte表示上边界。其支持如下类型:
| integer_range | float_range | long_range | double_range | data_range | ip_range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -2^31-2^31-1 |
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/range_index?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
请求
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/range_index/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
Text类型
Text被用于全文本搜索。建立索引前,text字段会通过analyzer将string切割成单独的term,而后对这些term建立索引。解析操作使得es能够搜索全文本中单独的词。text不能被用来排序并且很少用来分析。可以使用fields参数将一个字段同时赋予两个属性。
其常用属性,还有一些不常用的(用来使得text能够进行排序和agg,具体看官方文档吧)
| 参数 | 默认值 |
|---|---|
| analyzer | standard analyzer |
| boost | 1.0 |
| eager_global_ordinals | false |
| fields | |
| Index | True |
| index_option | positions |
| Index_phrases | False |
| Norms | True |
| position_increment_gap | 100 |
| Store | False |
| Search_analyzer | Analyzer |
| Term_vector | No |
token count类型
token是值进行分析后去切词。token count是一个整数,其接收string值,分析它们,之后索引在这个string中token数量。例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
其支持参数有
| 参数 | 默认值 |
|---|---|
| analyzer | |
| boost | 1.0 |
| doc_value | True |
| Index | False |
| Null_value | miss |
| Store | false |
映射参数(mapping parameters)
boost(升级)
使用boost参数,可以在计算相关性评分时对应字段自动提升。例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000002?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
此时匹配title字段的权重将是匹配content的两倍。boost默认是1.0
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/my-index-000002/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
不止能在创建索引是设置字段的boost,请求时也是可以的,如下请求和上述请求效果相同:
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/my-index-000002/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
不建议在索引中使用boost:
- 不能更改文档中字段boost的值,除非re-inidex。
- 想要实现加权的功能,在请求时也是可以的。
- 索引时间提升作为规范(norm)的一部分存储,只有一个字节。 这降低了字段长归一化因子的准确率,这可能导致较低的相关性评分计算。
doc_values
大部分字段默认被索引,这使得他们可以用来搜索。倒排索引通过term查询数据建立的倒排term,然后找到对应的文档。
但排序,聚合以及在脚本中访问字段需要使用不同的数据访问模式,他们通过文档来寻找对应字段中的term。
Doc values是当在构建文档时被存储在磁盘的数据结构,其存储与_source中相同的值,但以面向列的方式存储,这相对排序和聚合来说是更加高效的。几乎所有字段类型都支持Doc值,但text和annotated_text字段除外。
可以理解为,倒排通过term来查找到对应的文档,doc values通过文档来找到对应的字段,但倒排既然已经找到文档了,为啥还需要单独的doc values呢,不是可以直接通过倒排获取的文档来检索字段吗?答案是肯定的,确实可以这样,但这样效率是很低的,倒排获取的文档是_source。其被存储的时候是被压缩存储的,如果想要通过_source来获得字段内容,将会是更耗时的,因此倒排获取文档后,通过doc values可以直接获取对应字段值,这就大大加快速度了。
没有设置doc_value的字段不能被aggs和sort。
1 | curl -X PUT "http://10.138.35.116:8233/my-index-000018?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
index
是否字段是可以被索引的。其实就是是否建立倒排。大部分字段都是true。未建立index的字段是不可请求的(不可搜索)。
store
默认字段被索引使得其可以搜索,但不被(单独)存储。着意味着它们可以被请求但原始字段值不能被检索。通常这些字段都存在在_source字段中,因此可以使用检索_source之后添加source filteriing来实现对字段的检索。
在部分情况下,store一个字段是十分有用的。比如一个文档中存在title date字段和一个十分长的content字段,只想检索title,date字段而不想通过_source中提取(更快)。
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000003?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
store fields总是返回的数组。
另一个应用场景是对于一些不会被存储在_source中的字段。例如copy_to字段。
copy_to
copy_to参数可以将拷贝多个值到一个组中,此时能够作为一个单独的字段进行请求。典型的应用场景是,经常需要搜索多个字段,可以使用copy_to来减少请求的参数来实现加速。
例如:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000004?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
对于copy_to存在如下需要注意的点:
- 复制的是字段值而不是term
- 原始的_source字段将不会被修改以显示复制的值,即
copy_to拷贝到的字段(上例中的full_name)不会在_source中。 - 同一个字段可以拷贝到多个字段下。
- 不能进行递归copy
null_value
null值不能被用来索引或搜索。当一个字段被设置为null(或者空数组),被认为字段缺少值。
null_value参数允许替代一个显示指明的null值(不能是空数组)为特定值,这使得其可以被索引和搜索。例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000005?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
这里,第一个索引显示指明为null因此可以被NULL替换,第二个索引为[],不能直接替换。因此搜索时,只匹配第一个文档。
null_value设置的值需要与字段具有相同的数据类型。一个long字段不能有一个string的null_value.
null_value1只影响数据如何索引,其不会改变_source字段。
meta
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/mapping-field-meta.html
format
在json中,时间被存储为字符串。ES使用一系列的预定义格式识别并解析字符串为时间戳。除了基本的ES已构建的格式外,还支持用户自定义时间格式。具体包含的已构建的格式详见文档:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/mapping-date-format.html#built-in-date-formats
ignore_malformed(忽略畸形)
有时,我们对数据来源没有很好的把控,一个用户发送一个login字段可能是date,另一个用户发送的可能是邮件地址。
默认情况下,索引一个错误的数据类型进入一个字段会抛出异常,并拒绝整个文档。ignore_malformed参数如果被设置为true,异常将会被忽略,畸形的字段不能被索引,但其他字段都能够正常被处理。
例如:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000007?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
字段number_one被设置运行畸形数据,number_two被设置不允许有畸形数据。因此第一个文档索引可以成功,第二个将报错。
可以使用_ignored来统计畸形数据。
ignore_malformed不能被使用于如下类型的字段中:Nested,Object,Range。
eager_global_ordinals
doc_value(正排)并不是直接进行file-value的存储,而是存储一个序号,序号对应的是原始文本,看上去就是这样的结构:[_id-->num-->term]。但,每个文档的doc_value如果具有相同的值,则其对应的序号是一样的,这样可以方便压缩,而且利于后续处理。举例来说,在进行统计分析时,在分片层收集序号进入桶(buckets),随后在将结果进行联合时,转换序号到实际文本。
但是,对于一个索引来说,可以存在多个分片,此时每个分片的序号就不能完全保证唯一,为了解决这个问题,ES设置了统一的映射,被称为全局序号,全局序数映射基于分段序数建立,并且用来维护每个分段从全局序数到局部序数的映射。
使用eager_global_ordinals可以加速获取doc_value。(减少一次映射)。但是不建议使用(内存开销过大)。
ignore_above
当字符串长度超过ignore_above将不能被索引或存储。对于字符串数组来说,每个字符串都适用该规则。所有的字符串在_source都存在,但不能用来index和agg。
例如:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000008?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
在最终的agg中,搜索会返回所有文档,但只有第一个数据会存在agg中。
index_options
index_options控制什么信息被增加进入倒排索引中为了搜索和高亮的目的。index_options目的为了text字段,不建议其他字段使用该参数。
其接受如下参数:
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| docs | 只有文档编号被索引。能够回答某个term在该字段存在吗。 |
| freqs | 文档编号和term出现频率。term频率被用来计算相关性评分。 |
| positions(default) | 文档编号和term出现频率,以及term出现位置。位置可以用来邻近或词组查询。 |
| offsets | 文档编号和term出现频率,以及term出现位置,还有起始和终止的字符偏移。偏移用来加速高亮展示。 |
similarity
ES运行用户定义每个字段的相似评分。
用户自定义相似模块参考index中的相似。
ES定义了几个可以直接使用的相似模块:
BM25:默认相似。
classic:TF/IDF算法。
boolean:一个简单的布尔相似性,当不需要全文排名时使用,分数应仅基于查询词是否匹配。 布尔相似度使术语的得分等于其查询量。
fileds
处于不同的目的使用不同的类型来索引字段是十分常用的。这就是multi-fileds。例如,一个string可以使用text来进行全文本搜索,也可以作为keywords进行soring和agg。
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000009?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
city字段是text,能够进行全文本搜索,city.raw是keyword,可以用来排序和agg。
Multi-fields不影响_source字段。对于存在的字段可以使用put mapping API增加multi-field。
multi-field另一个使用场景是使用多个分析器去解析同一个字段,以此来优化文本相关性。例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000010?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
这里text字段使用默认的standard分析,其将文本切割成单独的字,text.english使用english分析,其将文本分割成每个单词的词根。在未指定search_analyer时,在搜索时使用的解析和索引时使用的解析是一样的。
这里,搜索是text字段使用standard解析,可以解析到foxes,text.english使用english分析,可以解析出fox。这样,可以让我们匹配到更多数据,但由于query中指定了foxes,因此fox的分数更低。
normalizer
normalizer专门未keyword使用,定义一系列操作,这些操作在文档索引前被执行,也在keyword字段作为被搜索时执行。例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000011?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
上述的搜索两个文档都会被检索出来,因为都是先执行了大小写转化。在使用agg是也是如此:
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/my-index-000011/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
返回
1 | { |
bar有两个。
analyzer
analyzer参数用来指明在索引和搜索时如何进行文斌分析。analyzer只用于text类型。除非覆写了search_analyzer否则搜索时使用的analyzer和索引时一样。
search_analyzer
默认情况下,搜索时对query的解析和在索引文档时应该是一样的,以保证query中的term和倒排索引中的term一致。
但有些时候,我们希望索引文档和进行搜索时使用不同的解析,这时可以使用search_analyzer参数来实现。
dynamic
默认情况下,能够动态的增加文档或文档中内部对象的字段,只需要在索引时添加即可。例如:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001/_doc/1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
该参数支持3个值:
- true:新字段发现后自动添加。
- false:新检测到的字段将被忽略。 这些字段不会建立索引,因此无法搜索,但仍会出现在返回的匹配的_source字段中。 这些字段不会添加到映射中,必须显式添加新字段。
- strict:检测到新字段将抛出异常。
dynamic设置可以在mapping级别上,也可以在内部对象中设置。内部覆盖外部。
properties
type(类型)映射、object fields(对象字段)和 nested fields(嵌入字段)包含的 sub-fields(子字段),称之为 properties(属性)。这些 properties(属性)可以为任意 datatype(数据类型),包括 object(对象)和 nested(嵌入数据)。属性可以通过如下方式添加:
- 在创建索引时确认。
- 显示的更新或者添加。(put mapping)
- 索引包含新字段的文档时动态的加入。
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
coerce
coercion用于清理脏数据来修复一个字段的类型。例如:
- string被编码为整数。
- float被截断为整数。
coerce只用于数值类型。开启时,如果传参不正确将会被编码,如果关闭,传参不正确,文档将被拒绝。例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000015?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
其中,1、2均能成功索引。3不行,因为不能编码成int。4也不行,由于指定不编码(值是10就可以)。经验证,coerce只是在内部对值进行了编码,可以让我们按照对应的类型进行使用(检索,分析),并不改变_source。
enabled
ES默认会尝试索引所有字段,但是有时,我们只是用来存储一些字段,不会用其进行搜索活分析,此时就不需要进行建索引和分析了。这时可以使用enable参数。enable能够被使用在任何object的顶层,此时,es会跳过对该object字段的解析。例如:
1 | PUT my-index-000001 |
此时表示session_data字段只进行简单存储,即diabled。
索引的整个map也可以是disabled的。例如:
1 | PUT my-index-000001 |
对于设置了disable的字段,即使索引一个文档的时候,传递的不是object类型,也能正常执行,因为es跳过对其解析。如下操作会成功:
1 | PUT my-index-000001 |
index_prefixes
该参数使得对应字段可以在索引数据是建立字段值前缀的索引来加速前缀搜索。其接受如下设置:
- min_chars索引的最小前缀长度,默认2.
- Max_chars索引的最大前缀长度。最大小于20,默认5。
例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
使用默认配置。
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
index_phrases
如果启用,则将两个词的单词组合索引到单独的字段中。 这样可以使精确的短语查询(无延迟)更有效地运行,但要以较大的索引为代价。 请注意,这在不删除停用词的情况下效果最好,因为包含停用词的短语将不会使用子字段,并且会退回到标准短语查询中。 接受true或false(默认)。
norms
norms存储了一系列归一化因子,这些被用于请求时计算文本相关性评分。norms会请求大量的磁盘。如果某个字段确定不需要进行文本相关性的计算,可以设置该字段为false。如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001/_mapping?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
position_increment_gap
分析的文本字段将term位置考虑在内,以便能够支持接近或短语查询。 当为具有多个值的文本字段建立索引时,将在值之间添加“伪”间隙,以防止大多数短语查询在值之间进行匹配。间隙大小通过参数position_increment_gap控制,默认100.
例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001/_doc/1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
第一个请求就会被匹配到文档,因为设置了间隙未默认100。第二个可以获得数据,由于设置的slop大于100。
term_vector
Term_vector包含由分析处理所产生的term信息。包括
- term列表
- positiions:每个term在源串的位置(或顺序)。
- offsets:起始和结尾的位置。
- payloads:有效负载(如果可用)—与每个term位置关联的用户定义的二进制数据。
其值如下:
| 值 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| no | 没有(默认) |
| yes | 只有term列表 |
| With_positiions | 对应上文部分 |
| With_offsets | 对应上文部分 |
| with_positions_offsets | 对应上文部分 |
| with_positions_payloads | 对应上文部分 |
| with_positions_offsets_payloads | 对应上文部分 |
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000019?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
元数据字段
_ignored
_ignored字段索引并存储在文档中由于开启ignore_malformed而被忽略的畸形字段名。该字段可以被搜索,使用term,terms,exits请求。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/my-index-000007/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
搜索存在一个或多个被ignored的字段文档。
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/my-index-000007/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
搜索存在mumber_noe,被ignored的文档。
_id
每个文档含有一个_id作为唯一标识。_id字段会建索引,因此可以通过get API或者ids query获取文档。_i也可以在索引文档时分配。该字段不可配置。
id可以通过term、terms、match和query_string请求
1 | # Example documents |
_id被限制使用分析和排序。如果想要实现,建议复制_id内容到另一个具有doc_value的字段中。
_id被限制长度为512字节。
_index
当跨多个索引执行查询时,有时需要添加仅与某些索引相关联的查询子句。该 _index字段允许在索引文档上进行索引的匹配。它可以在 term,terms 查询,aggregations(聚合) , scripts(脚本) , sorting(排序)中使用 :
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/index_1/_doc/1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
_routing
文档被路由到指定主分片通过如下函数
1 | shard_num = hash(_routing) % num_primary_shards |
默认情况下_routing取文档id。
用户也可以自己为每个文档指定_rounting,例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001/_doc/1?routing=user1&refresh=true&pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
对于指定routing的文档获取、更新或者删除操作都需要指定routing。
与_id一样,_routing也可以备用于请求,例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/my-index-000001/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
搜索时也可以指定routing,使得在指定的shard中进行搜索。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/my-index-000001/_search?routing=user1,user2&pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
由于指定routing时,对于其更新,删除和获取都需要指定,如果未指定将会导致一个文档被索引到多个分片,问了避免这个问题,可以在mapping中进行配置,对于没有指定routing的请求将抛出异常。
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000002?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
_source
_source存储了索引文档时原始的json内容。其不能被index,但会被store。
Dynamic mapping(动态映射)
对于在索引时增加的字段,ES会进行动态的映射。下面说一些简单的规则
| json类型 | ES数据类型 | |
|---|---|---|
| true\ | false | Boolen |
| float | float | |
| integer | long | |
| object | object | |
| array | 第一个非空值类型决定。 | |
| string | 如果通过时间格式校验,则说date,如果通过数值格式校验,则是double或long。否则就是text,并且有着keyword子字段。 |
索引模板
模板索引告知ES如何配置一个索引,当索引创建时。在创建索引之前先配置模板,然后在手动创建索引或通过对文档建立索引创建索引时,模板设置将用作创建索引的基础。
有两种模块,分别为索引模板和组件模板。组件模板可以被用来重复构建mapping,setting,aliases配置块。可以使用组件模板构建索引模板,组件模板不能直接运用到索引上。索引模板可以包含一系列的组件模板,与直接指明settiing,mapping,aliases是一样的效果。
如果一个数据流或者一个索引文档匹配到超过多个索引模板,会选择优先级最高的一个。
如果一个索引创建时指明了setting也品牌上了一个索引模板,指明设置的优先级更高。索引模板其实就是对于没有设置索引映射的时候选择的默认设置。例如:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/_component_template/component_template1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
其中priority字段指明索引模板的优先级。index_patterns指定了匹配的索引。
Text分析
text分析是是一个将非结构化的文本进行转换为结构化型式以加速搜索的过程。
text分析主要如下部分:
Tokenization
通过tokenization使得全文本搜索成为可能。tokenization拆开一个文本成更小的块,被叫做tokens。大多数情况下,tokens是单独的词。
Normalization
Tokenization将text切割成token,但每个token还是需要进行严格的匹配,这意味着Quick不能匹配quick,jumps不能匹配leaps(同义词)。为了解决这个问题,可以使用normalization进行转换成统一格式。
用户可以定制自己的text分析。text分析通过analyzer进行,其含义一套管理全局的规则。用户可以控制的分析步骤包括:
- 在tokenizatioin前对text进行变换。
- 如果将text转化为token。
- 在索引前对token采用何种normalization。
基本概念
analyzer内部剖析
一个analyzer,不论是内建的还是用户自定义的,都是由三部分组成。包括character filters(字符过滤),tokenizer和token filters。
character filter
字符过滤接收源text为一个字符流,并且能够在这个字符流中增加、删减或者更改字符。例如,一个字符过滤可以将印度阿拉伯数字(٠١٢٣٤٥٦٧٨٩) 转化为(0123456789),或者去除html中类似于<b>的元素。
一个analyzer可以由0个或多个字符过滤,会逐个执行。
Tokenizer
tokenizer接收字符过滤后的字符串作为数据流,切割他们成单独的tokens,并输出一个tokens流。例如,空格tokenizer按照空格将字符串进行切割。
tokenizer也负责记录每个term的数序和在源串中的起始和终止位置。
一个analyzer必须有一个指明的tokenizer。
Token filters
token过滤接收token流作为输入,可以增加、移出或者更改tokens。例如一个lowercase会将所有token转化为小写,stop token将移除停用词(像the),synonym将引入token的同义词进入token流,同义词位置和原词一样,可以会占多个位置,例如dns是domain name system同义词。
一个analyzer可以又0个或多个token filters,会逐个执行。
索引分析和搜索分析
文本分析发生在两个时候,索引文档时,text字段将被分析。在text字段上进行全文本搜索时,query串将被分析。
举例索引和搜索时使用同样的analyzer
使用空格token,并使用stop token stop和lowercase token stop。
索引一个文档包含text
1 | The QUICK brown foxes jumped over the dog! |
此时token为
1 | [ quick, brown, fox, jump, over, dog ] |
搜索时,query为
1 | "Quick fox" |
此时采用索引时同样的analyzer,将变为
1 | [ quick, fox ] |
此时能够匹配到quick和fox两个token。可以选取出索引的文档。
举例索引和搜索时使用不同的analyzer
ES如果被用来构建一个前缀匹配的搜索引擎。一个文档索引包含
1 | apple |
此时其包含的token为
1 | [ a, ap, app, appl, apple] |
搜索时,query为
1 | "appli" |
如果使用索引时的analyzer,其token为
1 | [ a, ap, app, appl, appli ] |
此时就能够匹配到apple,这是不合理的,这里应该将appli看做一个整体,此时就不能使用和索引相同的analyzer。
配置文本分析
测试analyzer
analyze api是十分方便的工具对于查看analyzer生成term。对应内建的analyzer可以如下使用:
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/_analyze?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
也可以联合测试各个部分
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/_analyze?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
对于用户定义的analyzer,可以通过如下方式进行测试。
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
使用内建analyzer
对于内建的analyzer可以直接使用,也可以在其基础上进行一定的增加。例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
创建自定义的analyzer
对于自定义的analyzer可以接受参数为
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| tokenizer | 一个内建的或者用户自定义的一个tokenizer |
| char_filter | 一个可选的数组,元素为内建的或者自定义的字符过滤。 |
| filter | 一个可选的数组,元素为内建的或者自定义的token过滤。 |
| position_increment_gap | 参考mapping部分同名参数。 |
例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
这里使用了mapping(指定字符)映射的字符过滤,使用了pattern(指定标点符号切割)的tokenizer,使用了停用词的token过滤。
最终,分析返回的结果为
1 | [ i'm, _happy_, person, you ] |
内建的analyzer
这里只简单介绍几个内置analyzer。具体查看https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/analysis-analyzers.html。
standard analyzer
standard分析器是默认的分析器,其提供了基于tokenization的语法,可以适用于大部分语言。
其支持如下参数
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| max_token_length | token的最大长度。如果超过,将按照该值进行切割token。默认255 |
| stopwords | 停用词。可以是预定义的停用词,如_english_,或者一个包含停用词的数组。默认为空。 |
| stopwords_path | 包含停用词文件路径 |
例如:
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000020?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
Pattern analyzer
pattern analyzer使用正则表达式对text进行切词。正则表达式默认为\W+。(所有非字母字符)。
例如
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/_analyze?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
切词后token为
1 | [ the, 2, quick, brown, foxes, jumped, over, the, lazy, dog, s, bone ] |
pattern支持参数为
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| pattern | java的正则表达式 |
| flags | java正则表达式的flags。 |
| lowercase | term是否转化小写。默认true |
| stopwords | 停用词。默认none |
| stopwords_path | 停用词文件路径。 |
例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:8233/my-index-000021?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
返回
1 | [ john, smith, foo, bar, com ] |
tokenizer介绍
tokenizer接收字符过滤后的字符串作为数据流,切割他们成单独的tokens,并输出一个tokens流。例如,空格tokenizer按照空格将字符串进行切割。
tokenizer也负责记录每个term的数序和在源串中的起始和终止位置、以及token类型,例如\<ALPHANUM> <HANGUL>, or <NUM>. 简单的analyzer只有 word 类型。
ES内建了大量可供用户自定义analyzer的tokenizer。
tokenizer要三种类型:将全文本切割为单独的词;将全文本或单个词切割为更小的片段(如前举例的前缀);用于结构化文本的,如email地址,路径,一般不一样全文本。
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/analysis-tokenizers.html 官网介绍了各个部分的tokenizer。由于对于中文支持一般,就不详细介绍了,有需要看官网吧。
这里介绍一下常用于测试的keyword kokenizer。
keyword kokenizer是一个“空”标记器,它接受给出的任何文本,并输出与单个术语完全相同的文本。 它可以与token过滤器结合使用以规范化输出,例如:
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:9200/_analyze?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
输出为
1 | [ New York ] |
Token filter介绍
ES也提供了一系列token filter供用户使用。https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/analysis-tokenfilters.html。具体查看官方文档。
character filter
HTML strip 字符过滤
HTML strip从文本中剥离HTML元素,并用其解码值替换HTML实体(例如,将&amp;替换为&)。
例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/_analyze?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
返回为
1 | { |
mapping 字符过滤
映射字符过滤接收一组KV对,进行替换。匹配时找最长品牌。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/_analyze?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
返回为
1 | { |
其参数为
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| mapping | KV数组 |
| mappings_path | 存储KV对的路径。可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对于config的相对路径。文件必须是utf8格式,且每一个key=>value单独占一行。 |
Pattern replace字符过滤
字符过滤类似于maping过滤,不过其使用的key为正则表达式。而且每个字符过滤只能有一个key,一个value。
其支持参数为
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| pattern | 要匹配的正则表达式 |
| replacment | 要替换的值,可以是正则表达式中匹配的元素。$1....$9 |
| flags | javaz正则表达式参数。 |
例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-00001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
返回为
1 | [ My, credit, card, is, 123_456_789 ] |
Normalizers
normalizer除了只作用于token纬度外与analyzer类似。nornalizer没有tokenizer单元,只有char filter和token filter的子集。其中包含arabic_normalization, asciifolding, bengali_normalization, cjk_width, decimal_digit, elision, german_normalization, hindi_normalization, indic_normalization, lowercase, persian_normalization, scandinavian_folding, serbian_normalization, sorani_normalization, uppercase。
例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/index?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
search data
执行搜索
使用search api来搜索和分析数据。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/bank/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
搜索超时
默认情况下,未设置超时时间限制,但在请求是可以添加超时参数,如果请求超时,将返回error
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/bank/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
也可以在 cluster settings API中设置集群默认超时时间。
track total hits
获取全部命中文档数量。想要获取全部的文档数量,只能进行全部文档的匹配,这是是否耗时的。track_total_hits参数使得我们可以控制如何进行统计。该参数可以给一个下边界,例如10000(默认值),此时告诉ES我们只想知道匹配的数量是否超过该值,当匹配到该值时,ES将停止匹配。这对于只想知道一个是否超过一个数值而不用具体数量来说是十分有用的。
当track_total_hits被设置为true时,表示进行完全匹配,统计全部。此时返回的total.relation是eq,表示total.value是全部匹配的数量。当track_total_hits是一个数值时,对于total.value的解释由total.relation决定。如果total.relation是eq,则表示匹配的数值小于设置的track_total_hits值,其total.value是实际匹配到的值,对于total.relation是gte,则表示匹配到的值大于total.value。
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/bank/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
检查是否有匹配的文档
如果只是想知道某个query是否有匹配的文档,可以设置size=0表示不关心搜索结果。也可以设置terminate_after为1表示匹配到第一个文档即通知检索。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/bank/_search?q=firstname:Amber&size=0&terminate_after=1&pretty" |
检索内部匹配(Retrieve inner hits)
对于含义父子结构和nested机构的数据,返回的文档起匹配的作用域不同。对于父子关系来说,父文档被返回可能基于匹配到的子文档,子文档被返回可能基于匹配到的父文档。对于含有nested的文档来说,我都被返回可能基于匹配到的nested类型。
上述情况,都是由于匹配的作用域与返回文档的作用域不一致导致文档被返回的原因被隐藏。很多时候,知道文档被返回的原因是十分有用的。此时,inner_hits特性就十分有用。该特性使得每一个搜索的文档返回时增加nested命中信息,里面用来展现实际匹配的作用域的内容。
其使用规则如下
1 | "<query>" : { |
这里<query>可以是nested,has_child,has_parent。
此时对应的每一个命中的返回信息类型下面的效果
1 | "hits": [ |
其支持的参数如下
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| from | 从返回的常规搜索匹配中每个inner_hits的第一个匹配获取位置开始的偏移量。(返回是从第几个开始展示) |
| size | 返回时每个inner_hits中匹配的最大数量,默认返回top3. |
| sort | 对于inner_hits中的匹配,按哪个字段排序。默认走评分排序。 |
| name | 被用于返回时指明内部命中的定义(字段)。当在一个单独的搜索请求中,多个内部命中字段被定义时是很有用的。默认情况下,对于父子关系来说,name是对于的关系名,对于nested来说,默认是nested路径。 |
Nested inner hits
1 | curl -XPUT "localhost:8233/test1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
其返回为
1 | { |
对于内部命中来说,其返回值相对于普通的hits内容,多了一个_nested结构。其中field表情匹配的类型字段,offset是当前返回的内容是在整个内部结构中的第几个(偏移量,从0开始)。由于排序的原因,其返回的偏移量和存储时可能不一致,这里展示的是存储时的偏移量。
nested inner hits and _source
对于nested来说,其不存在_source字段,由于其作为整个文档的一部分被存储。因此在nested inner hits中返回的_soirce是被解析出来的,这对于返回数据来说是十分耗时的,尤其是当设置的size超过默认值时。为了避免这部分开销,可以使inner hits不返回_source,而只返回我们关注的信息,这部分信息可以设置为doc value。例如
1 | curl -XPUT "localhost:8233/test1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
折叠搜索结果(collapse search results)
可以使用折叠搜索结果按照指定字段对搜索结构进行折叠(类聚)。折叠的结构只返回被折叠的数据中排序top1进行展示,对于每一个折叠的key。
例如,使用shopid对课程进行折叠,使用价格作为排序:
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/smart_edu_training_shop_course_index/_search?pretty" -H "Content-Type:application/json" -d ' |
返回是,匹配到的数量是文档的数量,而不是折叠后数量,折叠后的数量是未知的。用于折叠的字段一定是一个单独的keyword或者numeric,并且设置的doc_values属性。
折叠搜索不能和scroll、rescore以及search after联合使用。
折叠搜索结果可以和inner hits一起使用,用于展示搜索中被折叠的部分,例如
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/smart_edu_training_shop_course_index/_search?pretty" -H "Content-Type:application/json" -d ' |
上述可获机构名命中动物的机构下,价格最低的两节课(source本身和inner hits内部的source)。对于整个文档其排序和内部的排序可以指定不同类型,例如,上例中,会先按照sorce排序,再折叠,最后再排序。
当然也可以指定多种排序方式,例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/my-index-000001/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
分页搜索结果(pageinate search result)
默认情况下,搜索返回top10命中文档。可以使用search api中的from和size去分页大的结果集。from参数定义了跳过命中的数量,默认是0,size是最大返回数量。例如
1 | { |
应当避免使用from和size参数翻页太深(跳过太多)或者一次请求太多结果。搜索请求通常跨多个分片。每个分片都会装载其请求的命中和任何之前的页面进入内存,对于深的分页或者大的结果集来说,这是十分占用内存的。(网上说是:由于每个索引会存在多个分片,其为了获取指定排序的页面,就必须对每个分片进行排序,然后返回结果后交给统一的协调节点再进行排序,以获得最终结果。例如,存在一个索引存在5个分片,在搜索前10个的时候,其要保证每个索引都要取其排序的前10,再取10-20时,每个节点不能支取其自身的10-20,而是要取其前20,再交给协调节点,因此,对于很深或很大的数据来说,不但会导致大量的内存占用,而且排序时间也会大大提升。)
为了安全考虑,默认情况下,使用from和size进行翻页最深为1000。该限制被配置通过索引的index.max_result_window参数控制。如果需要访问超过1000的部分,可以使用seach_after。
Seach after
可以使用search_after参数使用上一页中的一组排序值来检索下一页匹配项。
使用serach_after用相同query和sort行多次检索时,如果一个refresh操作发生在两次请求之间,则会导致分页错误,解决方式为使用PIT(point in time,时间点)。
首先打开一个时间点:
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/bank/_pit?keep_alive=3m&pretty" -H "Content-type:application/json" |
返回pit的ID
1 | p66xAwEEYmFuaxZ2UHJReUlGb1REbXBsLXBKRjBWYUlnABZobXdNU0ZxalItR3hGZE01bkpiVURRAAAAAAAAAABJFlh4SnFRRFJsVDhhNk5CWXhxTGUwUlEBFnZQclF5SUZvVERtcGwtcEpGMFZhSWcAAA== |
指定排序进行一次搜索,讲PIT作为参数传递
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/_search?pretty" -H "Content-type:application/json" -d' |
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/bank/_search?pretty" -H "Content-type:application/json" -d' |
返回内容的最后一个命中文档的排序信息:
1 | [20,273] |
将最后一个文档的排序信息作为参数再次请求,并根据上一个返回更新pit的id。
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/_search?pretty" -H "Content-type:application/json" -d' |
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/bank/_search?pretty" -H "Content-type:application/json" -d' |
上面请求的时候第一个是使用了pit的,第二个是未使用pit的。
还有一个当前官方不太推荐的scroll,具体看官方文档吧。
过滤搜索结果(filter search results)
过滤搜索结果有两个地方可以实现:
- 使用boolean请求中,增加filter。此时搜索请求使用bool过滤对于搜索结果和统计(先过滤再统计)。
- 使用search api中的post_filter(后置过滤)参数。此时只针对搜索命中结果进行过滤,不影响统计(先统计再过滤)。
在后置过滤后可以使用rescore来重新算分,增强相关性。
后置过滤
后置结果主要用于统计,其可以在过滤前进行统计。例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/shirts?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
建立索引并写入数据。
要搜索guccci品牌下所以红色的裤子,但同事要统计gucci品牌下所以颜色的衣服以及gucci品牌下红色衣服的款式,可以使用如下请求
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/shirts/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
这里,要将颜色过滤放到统计之后,所以使用post_filter参数。
重新计算过滤结果评分( Rescore filterd search results)
重新计算评分可以提高精确度通过重新计算query和后置过滤返回的top文档,使用辅助(通常更昂贵)算法,而不是将昂贵算法应用于索引中的所有文档。
一个rescore请求会在每个分片返回数据到统一节点进行统一排序前被执行。
rescore请求只会在每个分片搜索结果经过后置过滤(如果有)返回前执行,其执行的数量被window_size参数控制,默认是10个。
默认情况下原始query评分会和rescore请求的评分进行线性想加来更新最终的_score。此时原始query和recore query的重要性通过参数query_weight和rescore_query_weight控制,默认是1。例如
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
两者评分被联合通过score_mode参数控制,其支持如下方式
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| total | 默认的线性加和方式。默认方式。 |
| multiply | 两个分数相乘。对于function query是十分有用的。 |
| avg | 平均分 |
| max | 取较大者 |
| min | 取较小者 |
也可以设置多个rescore过程,其执行逻辑为先执行第一,在执行第二个,依次执行。例如
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
排序搜索结果(Score search results)
可以依据指定的一个或多个字段对结果进行排序。可以指定每一个排序的顺序。使用_score是依据相关性评分进行排序,使用_doc是指名使用文档id进行排序。
例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
返回是,每个文档中会包含sort字段。指名该文档的排序值。
排序的参数order指名排序的顺序,asc指定递增顺序,dasc为递减。
对于数组或者多值的字段,mode参数控制如何对这种字段排序,其支持值为
| 值 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| min | |
| max | |
| sum | |
| avg | |
| median |
对于升序来说,默认取min,对于降序来说,默认取max。例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/my-index-000001/_doc/1?refresh&pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
排序中可以进行类型转换。例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/index_double?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
基于内部类型进行排序
ES支持基于排序的字段是文档内部的一个或多个元素,如nested。
对于nested排序支持参数有
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| path | 指定哪个nested字段被用来排序。实际的排序字段必须是此嵌套对象内的直接字段。 当按嵌套字段排序时,此字段是必填字段。 |
| filter | 一个过滤内部元素的过滤器,指定内部元素的哪些部分被用来计算评分。 |
| max_children | 选择排序值时,每个根文档要考虑的最大子级数。默认无限制 |
| nested | 与顶级嵌套相同,但适用于当前嵌套对象内的另一个嵌套路径。 |
例如
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
其排序根据供应商提高的蓝色的价格均值进行排序。
排序缺省值处理
对于排序中使用的字段,如果某个文档缺省,则可以使用miss参数指定的方式进行处理,其支持三个值_last和_first或者用户定义的值。默认是_last。
例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
排序忽略未映射字段
默认情况下,使用未映射的字段进行排序将会报错。unmapped_type可以用于处理该情况。指定了该参数,和其类型,则对于未映射的索引,将被认为存在该字段,但都缺省值,常用于多索引排序。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
此时,如果某个索引没有price字段,则被看作存在一个long类型的该字段,但都缺省该字段的值。
距离排序
搜索返回指定字段(Retrieve selected fields from search)
默认,搜索命中的文档返回数据包括_source字段,其包含建索引时所以信息。也可以指定返回的数据,而不用返回所有数据。可以在搜索时指定fields按要求返回指定数据:
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:9200/my-index-000001/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
fields基于mapping,因此其相交于_source有一定的好处,支持多类型字段(multi_fields)和别名。
在使用fields时,其实现是从_source中解析,_source被作为一个字段单独的存储在Lucene,所以要先取出_source再处理,这是十分耗时的。可以使用docvale_fields和stored_fields进行优化。对于指定索引返回字段包含如下5种方式。
Fields
fields运行获取一些列文档字段,其基于_source和mapping获取结果,对于时间字段来说,默认被格式化根据mapping的date format参数。例如
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:9200/my-index-000001/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
这里返回user.id和http.response下的所以字段,格式化@timestamp为epoch_millis格式。
返回时,只会返回叶节点,对于类型数据来说,也返回其叶节点,返回可能如下
1 | { |
Doc value fields
doc_values可以返回建索引是指定doc_values参数的字段。可以避免获取_source。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/my-index-000001/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
Stored fields
和doc_values,可以使用·stored_fields获取索引时指定store的字段。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
如果stored_fields为空,则只返回_id和_type。如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
Disable stored fields
可以将所以store全部禁用,使用_none_值,例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
此时_source和version都不会返回。
Source fileds
可以使用_source参数控制什么字段从source返回。设置为false表示不返回。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
Script fields
可以使用script_fields参数能够在数据返回一个脚本处理的结果。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
高亮(Highlighting)
高亮用来帮助我们标明搜索的文档为何被返回。其会在返回的文档中指定字段中添加高亮片段标识。例如请求:
1 | { |
返回为:
1 | { |
返回的高亮部分内容,会请求要展示的字段的真实内容,如果字段未被设置为store,则从_source中解析获取。
ES支持三种高亮,分别为unified,plain,fvh(fast vector highlighter)。可以在每个要标注高亮的字段上使用type参数选择。
unified
unified高亮使用Lucene的unified高亮。其将文本切割成片段,使用BM25算法对每个片段打分。为默认高亮方式。
Plain 高亮
Plain高亮使用Lucene的基础高亮。它试图从理解单词重要性和短语查询中的任何单词定位条件方面反映查询匹配逻辑。
fvh高亮
fvh使用Lucence fvh高亮。其可以使用在属性设置了term_vector为with_position_offsets的字段上。
偏移策略
ES实现高亮,需要知道匹配到的片段对应于原始文本中的位置,其获取方式有如下三种:
- The postings list。如果字段的
index_options被设置为offset,则unified直接使用建库时倒排中的位置信息,不要再次请求analyzing。其相比于term_vectors请求更少的磁盘。 term vectors.如果term_vector通过设置为with_position_offsets提供,则unified将使用term_vectors。- plain高亮。当没得选时,
unified将使用该策略,它会创建一个很小的内存索引,并通过Lucene的查询执行计划程序重新运行原始查询条件,以访问当前文档中的低级匹配信息。
参数
高亮在请求时可以被设置,可以设置全局级的,也可以设置字段级的(覆盖全局)。具体参考https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/highlighting.html#highlighting-settings。
搜索多个数据流和分片
搜索是,可以将多个分片看作单独的一个,进行整体的请求。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/my-index-000001,my-index-000002/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
索引提权,当搜索多个分片可,可以为每个分片赋予不同权重:
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
近乎实时搜索(near real-time search)
Lucene是ES基于的java库,它引入了按段搜索的概念。一个段(segment)类似于一个倒排索引,index在Lucene含义是一个段的集合加上一个提交点(commit point)。一个提交之后,一个新的段被增加到提交点并且缓存被清空。
文件系统缓存位于ES和磁盘之间。处于内存索引缓存中的文档(图1)被写到一个新的段(图2)。
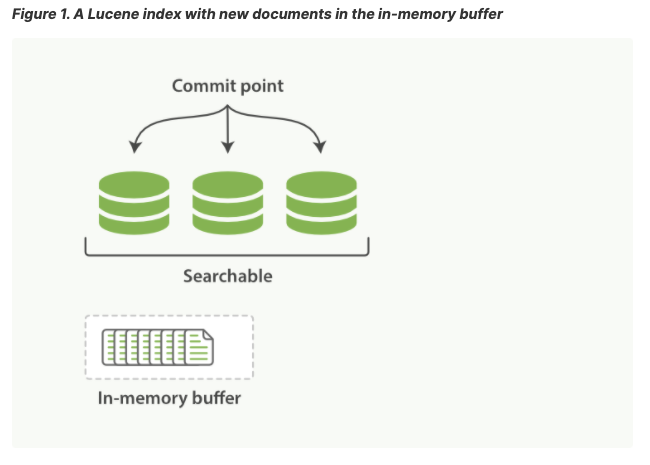
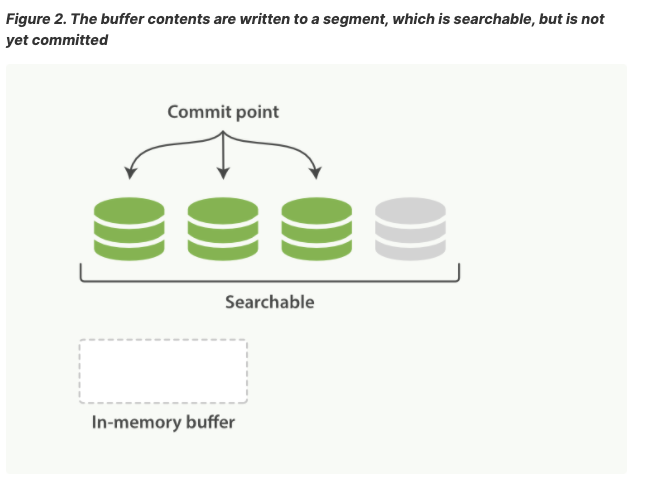
新的段首先被写到文件缓存(很廉价),之后被flush到磁盘(昂贵),在文件缓存时,文档即可开放和被读取,就想其他文件一样。
Lucene允许编写和打开新的段,使包含的文档可见。 与提交磁盘相比,此过程要轻松得多,并且可以经常执行而不会降低性能。
ES中写并且打开一个段落的操作被叫做refresh。一个refresh操作可以将一个分片上从上一次refresh到当前所以操作可在搜索中获得(生效)。可以使用如下操作实现refresh
- 等待自动refresh
- 请求中增加&refresh
- 使用Refresh API。
运行长期搜索
大部分搜索会很快返回结果,但有时,在数据量十分大时,可能需要消耗大量时间,因此可以使用异步请求获取结果。主要参考异步搜索。
Query DSL
ES提供一套基于JSON的请求语言DSL。可以认为请求DSL是一个AST(抽象语法树)。包含如下两个部分:
- 叶子查询子句(Leaf query clauses):在一个字段中查询一个特定值,例如
match,term或者range。 - 复合查询字句(Compound query clauses):包含其他的页查询字句,或者其他复合语句。被用来通过逻辑语句将多个查询进行联合(例如
bool,dis_max),或者改变他们的行为(例如constant_score)。
请求域和过滤域
默认情况下,ES返回命中的结果通过相关性评分排序。尽管每种查询类型可以不同地计算相关性分数,但是分数计算还取决于查询子句是在查询域上还是在过滤域文中运行。
query context
在查询域中,不仅决定一个doc是否命中,还会进行相关性评分的计算。只要查询子句传递一个查询参数(例如搜索API中的query参数),查询域就有效。
filter context
过滤域只会回答是或不是,不会进行相关性评分计算。只要查询子句传递一个过滤参数(例如bool查询中的filter或must_not参数),过滤域就有效。
例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
这里,对于title,contentz在bool下使用match匹配,是请求域,要进行评分的计算。status,publish_date在filter下,标识是过滤域,这里term和range都是被用于过滤。
复合查询(compound queries)
复合查询包含其他的复合查询或者页查询。
bool query
bool请求是默认的复合请求。bool请求被映射到Lucene的booleanQuery。其被构建通过一个或多个bool域,每个bool域含有一个类型,有如下类型可选择:
| 类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| must | 子句(query)必须出现在匹配的文档中,并会对评分做贡献。 |
| filter | 子句(query)必须出现在匹配的文档上,但不会对评分做贡献。过滤子句作用于过滤域,意味着评分被忽略,子句被考虑用于缓存。 |
| should | 子句(query)应该出现在匹配的文档中。 |
| must_not | 子句(query)必须不能出现在匹配的文档中。子句被执行在过滤域意味着评分被忽略,子句被考虑用于缓存。 |
bool请求采取的策略是越多匹配越好,每个匹配的must和should都会增加评分。
请求样例
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
其中minimum_should_match参数指定返回的文档必须匹配的should子句的数量或百分比。
如果在一个bool子句中包含至少一个should子句,并且没有must或者filter子句,minimum_should_match默认值是1,其他情况下默认值是0。
对于其他值可参考https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/query-dsl-minimum-should-match.html。
算分机制参考。
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
上述请求只有过滤域,可以所以返回的命中文档评分均为0.
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
上述请求除了一个过滤域,还包含match_all,match_all匹配所有文档,每个文档获得分值为1,因此,返回的文档评分均为1。
boosting query
boosing请求可以让我们控制相关性评分,其会返回匹配肯定的查询,同时降低匹配到否定查询文档的评分。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
其中,主要包含如下字段:
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| postive | 命中的文档必须匹配到内容 |
| negative | 命中的文档会根据配置降低评分。对于匹配postive的文档,boosting算分策略为。未匹配negative采用postive请求的算分,匹配到negative在positive的评分乘以negative_boost。 |
| negative | 一个0到1的浮点值,用来减少匹配negative的评分。 |
Constant score query
const_score包含一个过滤域,但可以指定其得分,而不是简单的过滤域的分数为0.例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
其支持的参数为
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| filter | 过滤域请求,不会算分。 |
| boost | 匹配filter的文档的相关性得分。默认是1.0。浮点数。 |
Disjunction max query
返回的文档匹配一个或多个被叫做请求从句的内嵌请求。如果一个文档匹配多个请求从句,dis_max请求会从匹配的请求从句中找到评分最高的,再在一定程度上加上其他匹配的请求从句的评分。
例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
dis_max支持的顶层参数:
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| queries | 包含一个或多个请求从句。返回的文档必须匹配至少一个。如果匹配多个,取相关性评分最高的。 |
tie_breaker |
可选参数。从0到1的浮点数。用来对于匹配多个请求从句时增加相关性评分使用。默认为0.0 |
对于匹配多个文档的请求,dis_max算分规则如下:
- 取相关性最高的请求从句的分数。
- 对于匹配的任何其他从句的分数,乘以
tie_breaker。 - 将上述两部分的分数想加。
Function score query
function_score能够使我们更改返回的文档的相关性评分。使用函数算分必须定义一个query和一个或多个函数,函数用来计算返回的文档分数。其使用例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
如果函数中没有filter,则表示匹配match_all":{}。即对返回的所以文档全部执行。首先:对于多个函数来说,参数score_mode指定如何将多个函数计算的评分进行联合。max_boost指定了函数算出的分最大限制,默认是无限制。boost_mode参数指定了对于函数算分生成的分数和原始请求返回的评分如何合并。默认情况下,函数算分不会影响召回的数据,即不会减少数据,但也可以指定min_score参数指定返回的最小分的文档,对于小于改值的文档将被过滤。
具体函数评分还有很多内容,详看:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/query-dsl-function-score-query.html
全文本请求(full text queries)
全文本请求用来搜索被分析的text字段。
match query
返回的文档匹配提供的文本,数字,日期或者bool值。被提供的text在匹配前先被解析(analyze)。
例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
match的顶层参数只有字段名(field),表示要检索的字段。
field支持参数为
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| query | 文本,数字,bool值或者日期希望在指定字段中查到的内容。query会先将请求经过analyzer切割成token,而不是拿一个完整的query进行请求。 |
| analyzer | (可选)转化text到token的analyzer。默认是在mapping中设置的search_analyzer。 |
| auto_generate_synonyms_phrase_query | (可选)默认是true。if为true,则match phrase请求将自动创建多个同义词。 |
| fuzziness | (可选)匹配中允许的最大编辑距离。(具体看REST API 中Common options) |
| max_expansion | (可选)query被解析出的term最大数量,默认是50. |
| prefix_length | (可选)对于模糊匹配时,其起始长度内保证匹配。 |
| fuzzy_transpositions | (可选)bool值,如果设置为true,则模糊匹配的编辑包括两个相邻字符的换位(ab→ba) |
| fuzzy_rewrite | (可选)如果fuzziness参数为0,则默认使用top_term_blended_freqs_${max_expansions},具体详看本章的rewrite部分 |
| lenient | (可选)bool值,如果是true则,则对于类型匹配错误则被忽略。如在一个数字字段上使用text进行请求。默认false。 |
| operator | (可选 string)OR(defalut),将请求的term进行取并集。AND,将请求的term进行取交集。 |
| minimum_should_match | (可选)解析出的term,返回的文档必须匹配数量。 |
| zero_terms_query | (可选string)如果请求被解析后没有一个term,是否应该返回文档。none(default):不返回文档。all:返回所有文档,等效于使用match_all。 |
由于只有query是必须的字段,因此可以简化请求,例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
即,对于field下,不用是一个结构。
match请求是bool请求,即请求文本被解析并构造一个boolean请求,元素为should。因此可以使用OR或AND进行连接,也可以设置minimum_should_match参数。
match phrase query(匹配词组请求)
match_phrase查询将分析文本,并从分析的文本中创建短语查询。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
类似 match 查询, match_phrase 查询首先将查询字符串解析成一个词项列表,然后对这些词项进行搜索,但只保留那些包含 全部 搜索词项,且 位置 与搜索词项相同的文档。
什么是短语
一个被认定为和短语 quick brown fox 匹配的文档,必须满足以下这些要求:
quick、brown和fox需要全部出现在域中。brown的位置应该比quick的位置大1。fox的位置应该比quick的位置大2。
通过加入slop参数,可以灵活的控制短语查询的,slop 参数告诉 match_phrase 查询词条相隔多远时仍然能将文档视为匹配。
例如
一个文档内容如下
1 | { |
搜索请求
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/bank/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
可以正常返回数据。
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/bank/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
无法正常返回数据。
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/bank/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
可以返回数据。
slop的使用基础是在建索引时包含的postion信息。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/_analyze?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
返回为
1 | { |
match phrese prefix query(匹配短语前缀)
返回的文档需要包含请求text中解析出的term,并且按照query本身顺序。最后一个term被当做前缀匹配。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
其顶层包含参数为字段名。
字段名下包含参数为
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| query | 需要分析的query。最后一个term被当做前缀匹配。 |
| analyzer | (可选)分析器。 |
| max_expansion | 最大允许解析出的term数量。 |
| slop | term直接允许的间隔,默认0 |
| zero_terms_query | 如果解析出无term,是否返回文档。 |
使用该请求有时会有问题。例如,一个请求是quick brown f。该请求首先基于quick和brown构建一个pharse请求。之后查看term存储字典,找到前50个前缀为f的term,增加这些term到先前生成的pharse请求中。这可能导致部分f开头的数据无法匹配。解决办法可以使用前缀匹配多加字符解决。
match boolean prefix query
一个match_bool_prefix请求分析输入文本到一个由term组成的bool请求。除了最后一个term外,其他term均是term请求,最后一个是前缀匹配。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
上试等价于
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
match_bool_prefix和match_phrase_prefix区别是,前者构建bool请求,后者构建短语请求。
match_bool_prefix支持的参数于match类似。
Intervals query(间隔查询)
返回的文档基于term顺序和间隔。间隔查询使用matching 规则,被构造成一个小的定义集合。该规则被应用在指定字段上。
下面的例子是返回文档中my_text字段中包含my favorite food,紧跟着是hot water,或者cold porridge。
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
intervals顶层参数:
field:希望搜索的字段。该参数的值是被用来匹配文档的规则object,基于matching term,顺序或者间隔。合理的规则包含如下值match,prefix,wildcard,fuzzzy,all_of,any_of。
match规则参数:
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| query | 请求的text |
| max_gaps | (int)解析出的term在匹配文档中的最大间隔。默认是-1,即无限制。0表示必须相邻。 |
| ordered | (bool)是否解析出的term要在匹配的文档中按顺序出现。 |
| analyzer | 如何解析query |
| filter | 过滤 |
| use_field | 更改作业的字段(没太理解有啥用) |
prefix规则参数
| 参数 | 值 |
|---|---|
| priefix | 前缀字段 |
| analyzer | 规则化prefix |
| use_field |
wildcard规则参数
通配符匹配运行最多匹配128个term,超出将报错
| 参数 | 函数 |
|---|---|
| pattern | 支持两个通配符?(任意单字符),*(0个或多个字符) |
| analyzer | |
| use_field |
fuzzy规则参数
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| term | 要匹配的term |
| prefix_length | |
| transpositions | |
| fuzziness | |
| analyzer | |
| use_field |
all_of规则参数
all_of规则匹配包含一个联合规则的匹配。
| intervals | |
|---|---|
| intervals | 一个规则数组,所以规则必须被都被匹配。 |
| max_gaps | 匹配term的最小间隔 |
| order | 是否要按顺序出现 |
| filter |
any_of规则参数
any_of规则返回任意一个子规则的间隔。
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| intervals | 规则数组 |
| filter |
filter规则参数
Multi-match query(多字段匹配)
multi-match构建match query对多个字段进行检索。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
可以指定在某个字段上提升权重
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
使用^对subject提权3倍。
如果没有指定fields,则匹配mapping中所有字段。
multi_match请求支持类型参数。可选类型为
| type | 含义 |
|---|---|
| best_fields | 使用match匹配任意一个文档,相关性评分取匹配的最高的一个。 |
| most_fields | 使用match匹配任意一个文档,相关性评分被各个字段联合。 |
| cross_fields | 使用相同的分析器将字段视为一个大字段。 在任何字段中查找每个单词。 |
| phrase | 在每一个字段上运行match_phrase请求。取最高分。 |
phrase_prefix |
在每一个字段上运行match_phrase_prifix请求,取最高分。 |
| bool_prefix | 在每个字段上运行bool_prefix请求,联合每个字段的结果计算最高分。 |
选取类型后,就可以确定对于于该类型实际对每个字段请求的语句,此时可以根据实际对每个字段的请求增加对应的参数。除了cross_fields以外,其他参数都是针对每个字段本身的,而cross_fields是将请求的字段全部看作一个整体,进行请求的。
例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
这个请求含义为,返回文档中first_name中必须出现Will和Smith,或者last_name中必须出现Will和Smith。
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
该请求含义是,返回的文档中first_name和last_name中必须出现Will和Smith。可以是一个中出现一个,也可以是两个都出现在一个里面。
具体更多细节看:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/query-dsl-multi-match-query.html
Term-level 请求
term级别的请求可以用来基于精准匹配来查询文档。不像全文本匹配,term级别的请求不会对文本进行分析,而是使用精准的匹配。term级别请求可以使用normalizer。
Exists query
查找指定字段包含value的文档。文档中字段无值可能有如下情况:
- 在原json中,字段为null或者[]。
- 在mapping设置了”index”:false。
- 长度超过ignore_above
- 值不是指定类型,并且设置了ignore_malformed
例如
1 | GET /_search |
空字符串也算有值。
fuzzy query
返回文档包含相似的term。使用编辑距离计算相似。
fuzzy顶层参数:field,作用于那个字段上。
field包含参数:
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| value | term值 |
| fuzziness | 具体看API convention中相应部分 |
| max_expansions | 允许的最大编辑距离 |
| prefix_length | |
| transposition | |
| rewrite |
例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
IDs
根据_id返回指定的文档,例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
prefix query
返回匹配前缀的文档。
例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
顶层参数:field
field支持参数:
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| value | 请求的前缀字符串 |
| rewrite | |
| case_insensitive | 设置为true时,允许值与索引字段值的ASCII大小写不敏感匹配。 默认值为false,这表示匹配的区分大小写取决于基础字段的映射。 |
例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
Range query
返回一个区间内的文档。
顶层参数:field
field支持参数
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| gt | > |
| gte | >= |
| lt | < |
| lte | <= |
| format | 转换日期格式数据 |
| relation | 标识对于range字段的查询提。INTERSCTS(default):匹配具有与查询范围相交的范围字段值的文档。,CONTAINS:使用范围字段值完全包含查询范围的文档进行匹配。,WITHIN:使用范围字段值完全在查询范围内的文档进行匹配。 |
| time_zone | 时区 |
| boost | 提权 |
例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
正常情况range使用在text和keyword上无效,由于search.allow_expensive_queries 被设置为false。
Regexp query
正则表达式匹配。
顶层参数:field
field参数
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| value | 正则表达式,具体看https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/regexp-syntax.html |
| flags | |
| case_insensitive | 是否区分大小写 |
| max_determinized_states | 查询所需的最大自动机状态数。 默认值为10000,Lucene将每个正则表达式转换为包含许多确定状态的有限自动机。 |
| rewrite |
注意:当search.allow_expensive_queries is set to false时,正在匹配请求将不会执行。
例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
Term query
返回匹配term的文档。应当尽量避免在text上执行term查询。因为text建term会经过一些列的处理,这会使查找文本字段值的精确匹配变得困难。在text上,应该使用match。例如,使用term搜索”Quick Brown Foxes!”,在text上就很难搜索到。
顶层参数:field
field支持参数
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| value | 要搜索的内容 |
| boost | 加权 |
| case_insensitive | 是否区分大小写 |
例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
Terms query
返回文档,包含一个或多个term。
顶层参数:field,boost。
例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
Terms set query
Terms set请求和terms请求类似,唯一一点是可以指定匹配term数量。
顶层参数:field
field支持参数
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| terms | term列表 |
| minimum_should_match_field | source中数字类型字段,用来指示匹配文档中需要匹配term数量。 |
| minimun_should_match_srcipt | 使用脚本标识需要匹配的term数量。 |
例如
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/job-candidates/_doc/1?refresh&pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/job-candidates/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
Wildcard query
通配符匹配。
顶层参数:field
field支持参数
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| value | 通配符表达式 |
| boost | |
| rewrite | |
| case_insensitive | 是否忽略大小写 |
if search.allow_expensive_queries is set to false.,执行通配符匹配无效。
例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
match all query
返回所以文档,并给予每个文档相关性评分1分。支持boost参数更改分数。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
Joining querys
ES支持两种join请求,分别支持nested数据和父子关系数据。
nested
封装另一个查询来搜素nested域。nested请求搜索nested域的object,就像他们是被独立索引的文档一样。如果一个object匹配搜索,则nested返回root文档(即整个文档)。
顶层参数:
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| path | 希望搜索的nested路径。 |
| query | 希望运行在nested的请求。 |
| score_mode | 相关性评分模式。有avg(default),max,min,none(0),sum。 |
| ignore_unmapped | 如果指定的path未映射,是否不返回文档,而不是错误。 |
举例一个多级别nested请求
1 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/drivers?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
父子关系
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/query-dsl-has-child-query.html
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/query-dsl-has-parent-query.html
rewrite parameter
该参数是给予专家提供的,其可以影响搜索执行流程和相关性评分。
ES使用 Apache Lucene来驱动索引和搜索。Lucene不支持如下请求:
- fuzzy(模糊)
- prefix(前缀)
- query_string
- regexp(正则)
- wildcard
Lucene转换这些请求到更简单的请求。例如bool请求或者bit set请求。
默认情况下,全文本匹配会将解析出的term构建出一个复合的bool请求。
rewrite控制如下内容:
- Lucene如何计算匹配到的文档的相关性评分
- 是否Lucene更改原始请求到bool请求
- 如果被转换为bool请求,哪个term应该被包括。
这里先补充一下Lucene的基本介绍。
Lucene介绍
Lucene包含如下概念:
Document: 它是在索引和搜索过程中数据的主要表现形式,或者称“载体”,承载着我们索引和搜索的数据,它由一个或者多个域(Field)组成。
Field: 它是Document的组成部分,由两部分组成,名称(name)和值(value)。
Term: 它是搜索的基本单位,其表现形式为文本中的一个词。
Token: 它是单个Term在所属Field中文本的呈现形式,包含了Term内容、Term类型、Term在文本中的起始及偏移位置。
Apache Lucene把所有的信息都写入到一个称为倒排索引的数据结构中。这种数据结构把索引中的每个Term与相应的Document映射起来,这与关系型数据库存储数据的方式有很大的不同。下面看看一个简单的倒排索引是什么样的,假定我们的Document只有title域(Field)被编入索引,Document如下:
- ElasticSearch Servier (document 1)
- Mastering ElasticSearch (document 2)
- Apache Solr 4 Cookbook (document 3)
| Term | count | Docs |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 1 | <3> |
| Apache | 1 | <3> |
| Cookbook | 1 | <3> |
| ElasticSearch | 2 | <1><2> |
| Mastering | 1 | <1> |
| Server | 1 | <1> |
| Solr | 1 | <1> |
每个词都指向它所在的文档号(Document Number/Document ID)。这样的存储方式使得高效的信息检索成为可能,比如基于词的检索(term-based query)。此外,每个词映射着一个数值(Count),它代表着Term在文档集中出现的频繁程度。
每个索引被分成了多个段(Segment),段具有一次写入,多次读取的特点。多个段是可以合并的,这个合并的过程称为segments merge。经过强制合并或者Lucene的合并策略触发的合并操作后,原来的多个段就会被Lucene创建的更大的一个段所代替了。很显然,段合并的过程是一个I/O密集型的任务。这个过程会清理一些信息,比如会删除.del文件。除了精减文件数量,段合并还能够提高搜索的效率,毕竟同样的信息,在一个段中读取会比在多个段中读取要快得多。但是,由于段合并是I/O密集型任务,建议不好强制合并。
Lucene默认打分算法
文档得分是一个用来描述查询语句和文档之间匹配程度的变量。Lucene默认的打分机制:TF/IDF(term frequency/inverse document frequecy)算法。
匹配文档的打分因子包含如下部分:
- 文档权重(Document boost):在索引时给某个文档设置的权重值。
- 域权重(Field boost):在查询的时候给某个域设置的权重值。
- 调整因子(Coord):基于文档中包含查询关键词个数计算出来的调整因子。一般而言,如果一个文档中相比其它的文档出现了更多的查询关键词,那么其值越大。
- 逆文档频率(Inerse document frequency):基于Term的一个因子,存在的意义是告诉打分公式一个词的稀有程度。其值越低,词越稀有(这里的值是指单纯的频率,即多少个文档中出现了该词;而非指Lucene中idf的计算公式)。打分公式利用这个因子提升包含稀有词文档的权重。
- 长度归一化(Length norm):基于域的一个归一化因子。其值由给定域中Term的个数决定(在索引文档的时候已经计算出来了,并且存储到了索引中)。域越长的文本越长,因子的权重越低。这表明Lucene打分公式偏向于域包含Term少的文档。
- 词频(Term frequency):基于Term的一个因子。用来描述给定Term在一个文档中出现的次数,词频越大,文档的得分越大。
- 查询归一化因子(Query norm):基于查询语句的归一化因子。其值为查询语句中每一个查询词权重的平方和。查询归一化因子使得比较不同查询语句的得分变得可行,当然比较不同查询语句得分并不总是那么易于实现和可行的。
Lucene打分不是完全概念上的TF/IDF打分机制,其实际公式如下:
从前面的公式中可以提炼出以下的几个规则:
- 匹配到的关键词越稀有,文档的得分就越高。
- 文档的域越小(包含比较少的Term),文档的得分就越高。
- 设置的权重(索引和搜索时设置的都可以)越大,文档得分越高。
查询重写
从本质上上,任何的查询都可以视为对多个关键词的查询。ElasticSearch(实际上是Apache Lucene很明显地)对用户的查询进行了重写,这样做是为了保证性能。整个重写过程是把从Lucene角度认为原始的、开销大的查询对象转变成一系列开销小的查询对象的一个过程。
这里以前缀查询举例。
首先索引数据
1 | curl -XPUT 'localhost:8233/clients/client/1' -d |
查询所有以字符 j 开头的文档:
1 | curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/clients/_search?pretty' -d '{ |
返回数据为
1 | { |
在Lucene中,根据索引数据建立的倒排为
| Term | Count | Docs |
|---|---|---|
| jack | 1 | <3> |
| jane | 2 | <2><5> |
| joe | 1 | <1> |
| rob | 1 | <4> |
跟踪ElasticSearch和Apache Lucene的源码,就可以看到prefix query重写成为如下的Lucene query:
1 | ConstantScore(name:jack name:jane name:joe) |
这意味着我们的前缀查询(prefix query)重写成了一个常量得分查询(constant score query),即由3个term query组合而成的布尔查询(bool query)。即Lucene所做的就是列举索引中存在的以j为前缀的关键词,并且每个词都构建出一个query对象。如果将重写后的查询与没有重写的查询进行比较,可以看到使用重写后的查询会使系统的性能有所提升,特别是在不同关键词数量较多的索引中。
如果我们自己手工构建一个重写的查询,其结果可能如下所示
1 | { |
可选改写值
scoring_boolean:该重写方法将对应的关键词转换成布尔查询的布尔Should子句,它有可能是CPU密集型的(因为每个关键词都需要计算得分),而且如果关键词数量太多,则会超出布尔查询的限制,限制条件indices.query.bool.max_clause_count
constant_score_boolean:该重写方法与上面提到的scoring_boolean重写方法类似,但是CPU消耗要低很多,因为它不计算得分,每个关键词的得分就是查询的权重,默认是1,也可以通过权重属性来设置其它的值。与scoring_boolean重写方法类似,该方法也受到布尔查询数量的限制。
top_terms_N:该重写方法将对应的关键词转换成布尔查询的布尔Should子句,同时保存计算得分。只是与scoring_boolean不同点在于,它只保留前N个关键词,来避免触发布尔子句数量的上限。
top_terms_boost_N:该重写方法与top_terms_N类似,只是得分的计算只与权重有关,与查询词无关。
top_terms_blended_freqs_N:该重写方法将对应的关键词转换成布尔查询的布尔Should子句,同时保存计算得分。与scoring_boolean不同点在于,它只保留前N个关键词,来避免触发布尔子句数量的上限,并且计算相关性评分时,所有term被看作有相同的词频,取所有匹配到的term中最大的那个词频。
constant_score(default):当匹配的term很少时,使用constant_score_boolean模式,否则,该模式按顺序查找匹配的term,并按照bit set(位集)返回匹配的文档。(应该是方便进行归并)。
Aggregations
聚类(aggregation)用来分析数据。es提供三种聚类:metric(数学计算),bucket(桶),Pipline(流水线)。
运行一个聚类
1 | GET /my-index-000001/_search |
在my-field字段上统计term。统计返回为
1 | { |
可以使用query参数来限制统计运行在指定范围的文档:
1 | GET /my-index-000001/_search |
这里会先执行query,获取指定的文档,在执行统计。可以使用post_filter执行后置过滤,即先统计,再过滤。
可以在请求中设置size=0,只返回统计结果:
1 | GET /my-index-000001/_search |
运行多个聚类
1 | GET /my-index-000001/_search |
运行子聚类
1 | GET /my-index-000001/_search |
执行子聚类
桶(bucket)聚类支持桶或数字计算的子聚类。例如,下面的请求聚类my-field类目的同时计算每个类目对应文档的my-other-field平均值。聚类是不限等级和深度的。
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/my-index-000001/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
响应可能如下
1 | { |
聚类中使用脚本
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/my-index-000001/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
如果指定了字段,可以使用_value来指代其值,可以使用value_type参数指名脚本生成的值,或者未映射的字段。
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/my-index-000001/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
Bucket aggregation
桶聚会创建文件的桶,每个存储桶都与一个标准(取决于聚合类型)相关联,该标准确定当前上下文中的文档是否“落入”其中。换句话说,桶聚合定义了文件集合。在桶聚合的子聚和中可以使用桶聚合或者数字聚合。
REST APIs
API convention(API公约)
Common options
Fuzziness(模糊)
一些请求支持非精准的模糊匹配,通过使用fuzziness参数。这里的模糊匹配是指对于每个term进行模糊匹配。
对于请求text和keyword字段,模糊匹配就是使用编译距离(动态规划计算),计算离线建的索引term和query解析的term距离。
fuzziness可选值为
| 值 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 0,1,2 | 最大允许的编译距离 |
| AUTO | 基于term长度进行控制允许的编辑距离。AUTO:[low],[high]。如果没有指定low和high则默认是3,6。含义为term长度小于3时,精准匹配。[3,5]允许一个编辑距离。[6,+)两个编辑距离。 |
例如数据中存在很多地址包含Street,此时请求:
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/bank/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
可以返回数据。
请求如下
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/bank/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
无命中文档。
Search APIs
Point in time(时间点)
似乎旧版本的es不支持。
默认情况下,搜索请求针对目标索引的最新可见数据执行,这称为时间点。ES的PIT是启动时数据状态的轻量级视图。有时,为了保证多次搜索的结果一致性,需要使用PIT,例如search after。
一个PIT使用前必须先被明确的打开。keep_alive参数指明该PIT存活时间,例如如下操作:
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/test1/_pit?keep_alive=1m" |
这里1m为1分钟。其返回为PIT的id
1 | { |
此时PIT的id讲被作为搜索请求的参数进行传递:
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/_search?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
对于存在pit参数的请求来说,不能指定index,routing,preference参数,由于这些参数都会从PIT中获取到。
keep_alive参数告诉ES,该PIT应该被延长存活时间多长。
开放时间点请求和随后的每个搜索请求可以返回不同的id。 因此,始终将最近接收到的ID用于下一个搜索请求。
通常,ES内部merge程序会通过merge小的断路到新的,更大的段落来优化索引。一单小的段落不再需要时,将会被删除。然而,打开时间点避免其被删除,直到其不再使用。
可以使用如下命令查询节点打开的时间点数量
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/_nodes/stats/indices/search?pretty" |
其中返回的open_contexts字段表示打开了多少个时间点。
默认情况下,时间点时间超过其存活时间就好自己kill。但我们也可以手动kill,命令如下
1 | curl -X DELETE "localhost:8233/_pit?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
返回
1 | { |
异步搜索
异步搜索可以让我们先提交搜索请求,后监控处理,再获取结果。
提交异步搜索API
异步搜索和同步搜索的搜索接受相同的参数和请求体。将search换成_async_search即可。例如
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:9200/sales*/_async_search?size=0&pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
响应包含一个id标识正在执行的搜索。可以使用id获取最终搜索结果,同时也会返回当前已获取到的结果,例如:
1 | { |
id是搜索标识。
is_partial标识在搜素执行完成后,搜索是否在所以分片上均成功了,或者失败。搜索在执行时,该值为true。
is_runing标识搜素是否完成。
response._shards.total搜索将在多少分片上执行。
response._shards.successful搜索当前已经在多少分片上成功执行。
response.hits.total.value当前搜索到的匹配文档数量。
当搜索完成时,is_runing将是false。但返回内容,可能只是部分,如果某些分片返回结果后搜索失败,或者协调异步搜索的节点死亡,则会发生这种情况。
使用wait_for_completion_timeout参数可以阻止并等待知道搜索完成或到达超时时间,其默认为1秒。在时间内完成搜索,将不会包含作为存储结果在集群内标识的id。keep_on_completion参数默认是false,当其为true时,即使在指定时间内返回,用户将结果存储在集群内。例如
1 | curl -X POST "localhost:8233/*/_async_search?wait_for_completion_timeout=20ms&pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d' |
返回为
1 | { |
对于搜索结果存储在集群的时间,可以通过keep_alive参数设置,默认是5天。时间单位可参考https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/common-options.html#time-units。
获取异步搜索返回结果
使用get api即可。例如
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:8233/_async_search/FndhdzJIMlJOUjhlem91ZTJyTWYzekEeaG13TVNGcWpSLUd4RmRNNW5KYlVEUTo0OTQxMTE3?pretty" |
返回可能为
1 | { |
response.num_reduce_phases:指示执行了多少次结果缩减。 如果该数字与上次检索到的结果相比有所增加,则可以预期搜索结果中将包含其他结果。
在获取结果时,也可以再次指定wait_for_completion_timeout和keep_alive。
删除异步搜索
当搜索还在运行时,delete将被忽略,否则,搜索返回结果将被删除。
1 | curl -X DELETE "localhost:9200/_async_search/FmRldE8zREVEUzA2ZVpUeGs2ejJFUFEaMkZ5QTVrSTZSaVN3WlNFVmtlWHJsdzoxMDc=?pretty" |